Drainage Basins
Explain the drainage basin as an open system with inputs, outputs, flows and stores
Drainage Basins
Explain the drainage basin as an open system with inputs, outputs, flows and stores
Summary
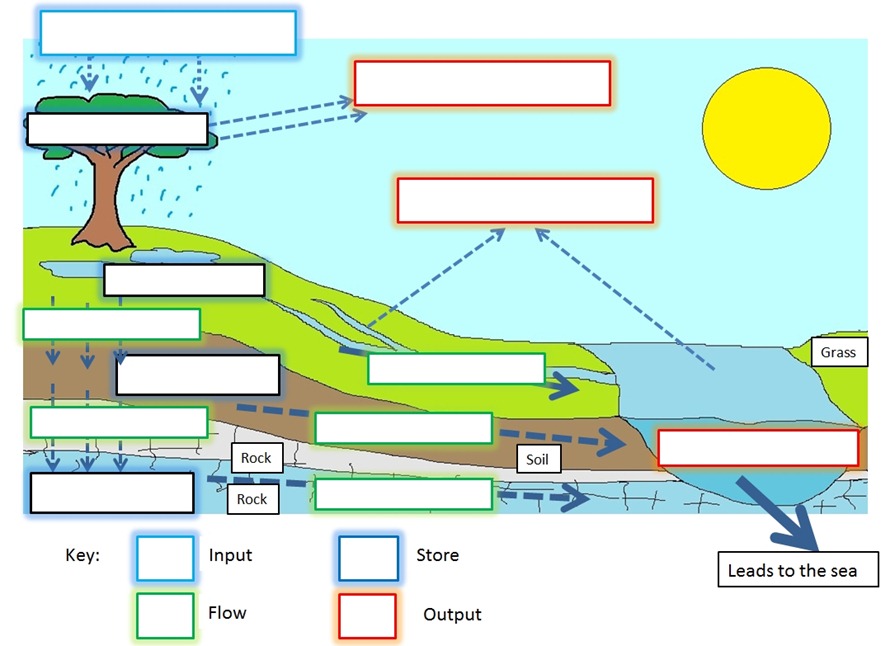
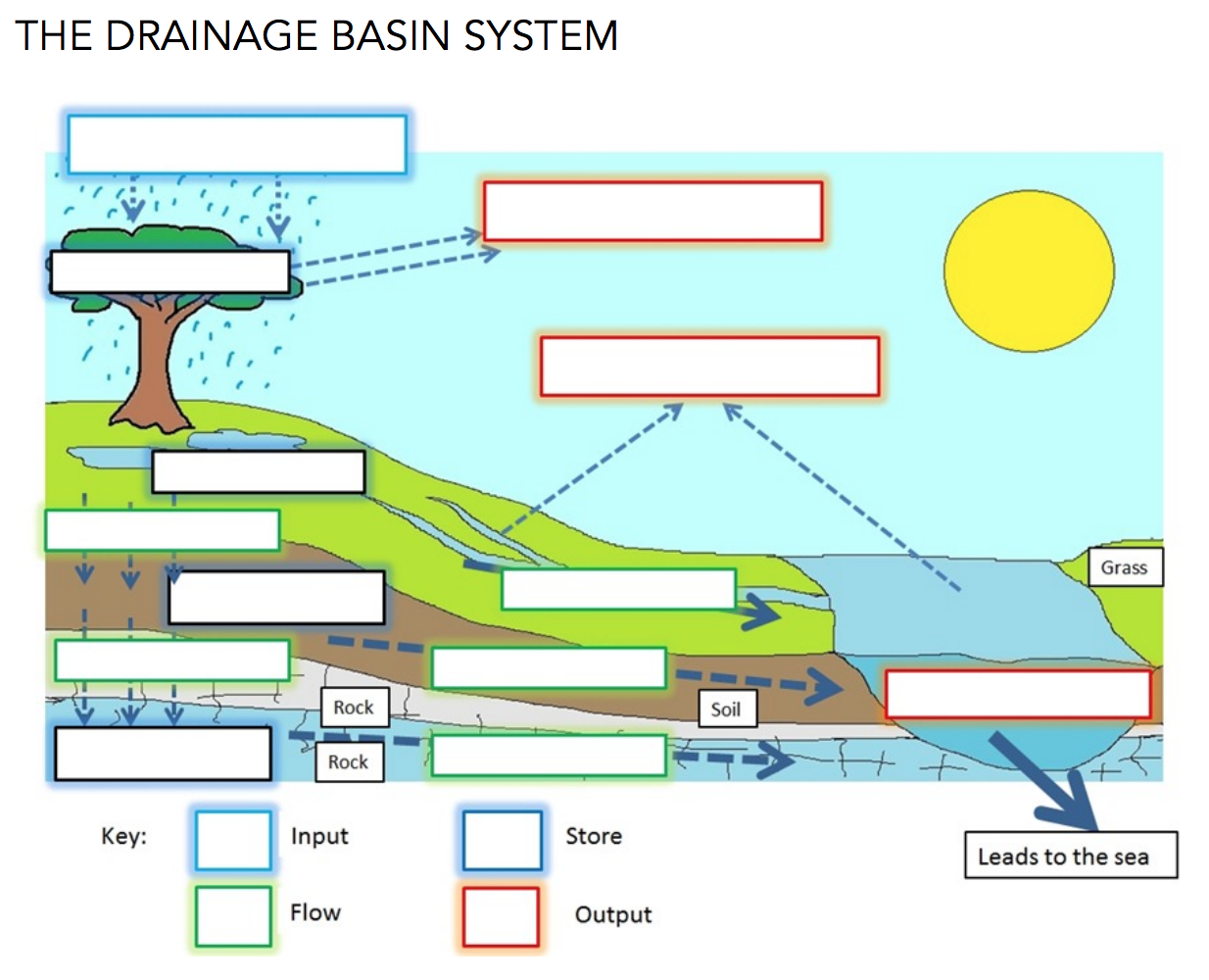
Drainage basins are open systems, with inputs, stores and outputs. The main input is precipitation which is regulated by various means of storage. Outputs include channel runoff, evapotranspiration and groundwater flow.
The Drainage basin system
Drainage basin flow chart
TASK
Complete the system diagram using information from the flow chart
Identify and annotate a feedback loop on your system diagram
Explain how human activity can modify 3 named processes on the diagram
PLENARY
Match the words with the definitions to create a circle

Discharge
Define river discharge and its relationship to stream flow, channel characteristics and hydraulic radius
Discharge
Define river discharge and its relationship to stream flow, channel characteristics and hydraulic radius
Add post-it notes to the board to identify the different inputs, processes, stores and outputs involved in the drainage basin system. How might human activity affect these?
RIVER DISCHARGE
River discharge is the volume of water flowing through a river channel. This is the total volume of water flowing through a channel at any given point and is measured in cubic metres per second (cumecs). Discharge is calculated as follows:
River discharge = mean velocity of water x cross sectional area of a river
The Bradshaw Model
Describe three relationships shown on the diagram above e.g. as discharge increases, velocity increases
HYDRAULIC RADIUS & RIVER EFFICIENCY
The wetted perimeter of a river refers to that part of the channel that is in contact with water. It represents the friction that slows down the river velocity. The longer the wetted perimeter, the more friction between channel and water.
The hydraulic radius is a measure of efficiency in a river channel. It is calculated by comparing the wetted perimeter with the cross-sectional area of the channel. The higher the hydraulic radius, the more efficient the river.
Hydraulic radius = cross-sectional area / wetted perimeter
Calculate the hydraulic radius for the two rivers below. Which river is more efficient?
ACTIVITIES
Make simple sketches of the diagram above
Read pp 7-10 (River Discharge) and make detailed notes under the different headings.
PLENARY
Explain how stream discharge is related to channel size and shape. [6 marks]
Award [1 mark] for defining/calculating discharge.
Award [1 mark] for establishing a link between discharge and channel size (e.g. higher discharge in a larger/lower course channel).
Award [1 mark] for establishing a link between discharge and channel shape (lower discharge in wide, shallow or deep, narrow channels, or equivalent point made).
The remaining [3 marks] should be awarded for explanatory points, such as:
role of hydraulic radius
importance of wetted perimeter
idea of friction in relation to stream efficiency
further development of width/depth or shape explanation.

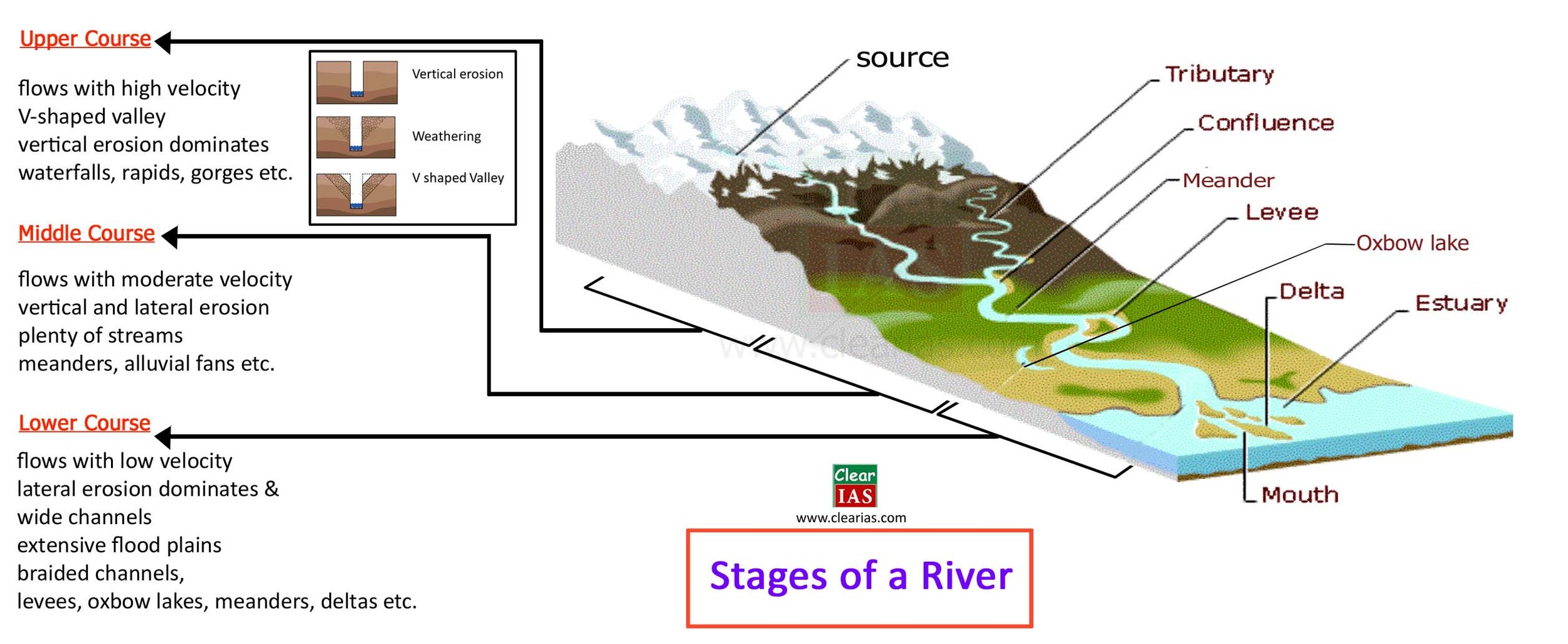
Stream Processes & Landforms
Describe and explain river processes of erosion, transportation and deposition and spatial and temporal factors influencing their operation, including channel characteristics and seasonality
Describe and explain the formation of typical river landforms, including waterfalls, floodplains, meanders, levees and deltas
Stream Processes & Landforms
Describe and explain river processes of erosion, transportation and deposition and spatial and temporal factors influencing their operation, including channel characteristics and seasonality
Describe and explain the formation of typical river landforms, including waterfalls, floodplains, meanders, levees and deltas