Geologic Time
Be able to name a range of geologic periods and describe the main geological and biological events
Geologic Time
Be able to name a range of geologic periods and describe the main geological and biological events
TASK 1: Write a list of major events of life on earth that you predict will be in this short video.
TASK 2: Add illustrations to show the major geological and biological events for the geologic eras below. Research each of the eras online and add further information about the geological and biological events in these eras.
TASK 3: Research the following eras and add information about geological and biological events to your timeline.
Pre-Cambrian (4600-538 mya)
Paleozoic (538-251 mya)
Mesozoic (252-66 mya)
Cenozoic (66 mya - today)

Earth Structure
Describe the characteristics of the internal layers of the earth
Earth Structure
Describe the characteristics of the internal layers of the earth
STARTER: With a partner, draw a labelled diagram of the internal structure of the Earth and share this with the class.
TASK 1: Watch the video and note the main information about the internal structure of the earth
TASK 2: Draw a labelled diagram of the earth's internal structure.
TASK 3: Read and highlight the text about the internal structure of the earth. Complete the gap fill exercise in the second document.
TASK 4: Watch the video and summarise the evidence for plate movement

Rock Cycle
Explain the processes responsible in the formation of igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic rocks
Rock Cycle
Explain the processes responsible in the formation of igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic rocks
TASK 1: Draw a labelled diagram of your understanding of the water cycle onto an A4 piece of paper. Share this with the class.
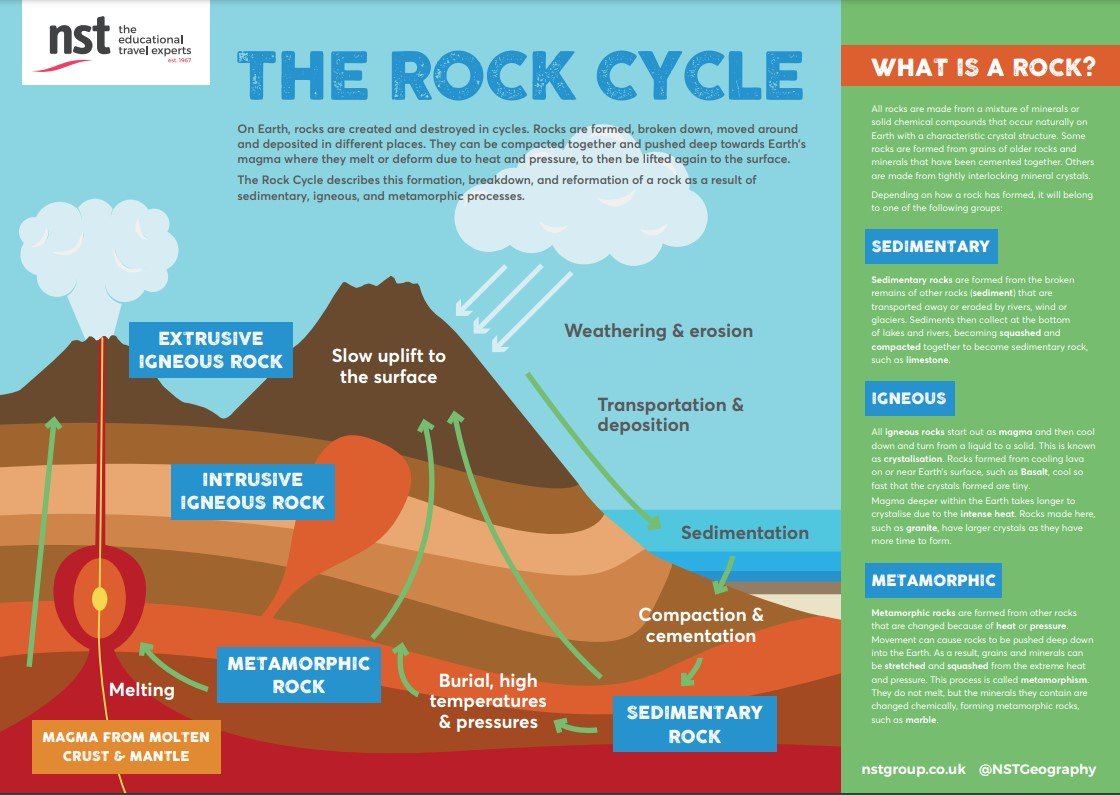
THE ROCK CYCLE
The rock cycle is a series of processes that create and transform the types of rocks in Earth’s crust.
There are three main types of rocks: sedimentary, igneous, and metamorphic. Each of these rocks are formed by physical processes—such as melting, cooling, eroding, compacting, or deforming—that are part of the rock cycle. (Source)
TASK 2: Study the diagram below and complete the accompanying process diagram.
TASK 3: Explore the resource below
TASK 4: Read document 1 and complete document 2
TASK 5: Study the resources below. Make a summary of each rock type.

Limestone Landscapes
Identify, describe and explain the formation of limestone features
Limestone Landscapes
Identify, describe and explain the formation of limestone features
TASK 1: Summarise the main geological regions of Switzerland
Switzerland can be divided into four geological units from north to south:
Tabular Jura and Folded Jura in the north and northwest, composed of limestone, marl (mixed rock composed of limestone and clay), clay, and anhydrite/gypsum
Swiss Plateau and “Molasse basin”; the latter, filled with erosion debris from the mountains, consists of sandstone, silt and marl
Northern Alps and Helvetic Domain, which consists mainly of calcareous and marly sediments from the Mesozoic
Central and Southern Alps with crystalline basement, mainly granites and gneisses, resulting from the recrystallisation due to the solidification of magma in the basement.
TASK 2: Watch the video and write a paragraph explaining the creation of the Alps
TASK 3: Watch the video below and make notes on the processes and landforms of limestone landscapes
TASK 4: Research limestone formations and complete the grid below
TASK 5: With the help of Atlas Mondial Suisse, colour in the map below to show the regions of Switzerland where limestone is abundant. Add a title and a key.
TASK 6: Watch the video and answer the questions below.
Name the material that limestone is made of.
Name the process that weathers limestone.
Explain why this process happens more quickly in tropical regions.

Geomorphology
Explain the main types of erosion and transportation by water, ice, wind.
Identify typical examples of glacial, fluvial and coastal landforms.
Show the positive and negative aspects of environments on human activities.
Geomorphology
Explain the main types of erosion and transportation by water, ice, wind.
Identify typical examples of glacial, fluvial and coastal landforms.
Show the positive and negative aspects of environments on human activities.
Geomorphology or geomorphic processes continually shape the Earth's surface / crust, and generate the sediments that circulate in the Rock Cycle.
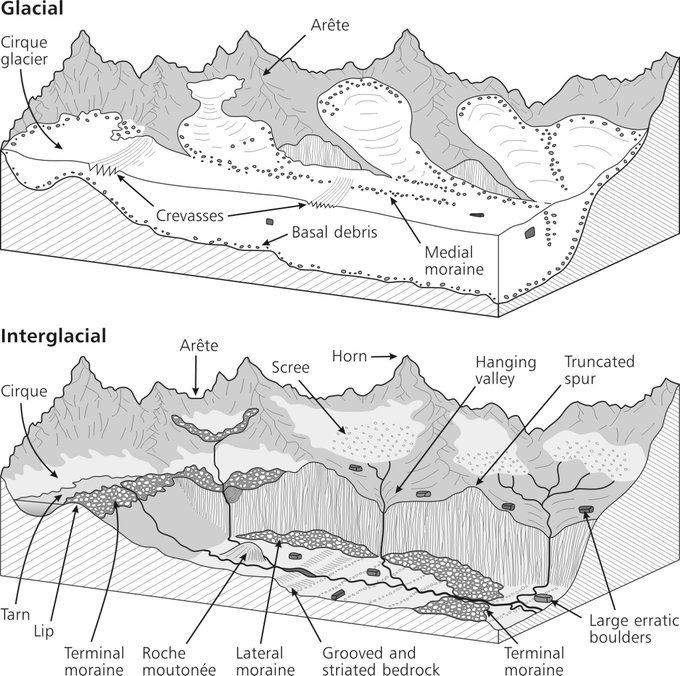
TASK 1: GLACIERS - PROCESSES OF EROSION & TRANSPORT
Watch the videos below and draw labelled diagrams to explain the processes of erosion, transport and deposition in glacial areas.
TASK 2: GLACIERS - LANDFORMS OF EROSION & DEPOSITION
TASK 3: RIVERS - PROCESSES OF EROSION & TRANSPORT
Watch the tutorials below and draw a labelled diagram to explain processes of erosion and transport in rivers.
TASK 4: RIVERS - LANDFORMS OF EROSION & DEPOSITION