Population Growth
Describe and give reasons for the rapid increase in the world’s population
Population Growth
Describe and give reasons for the rapid increase in the world’s population
Describe and explain global population growth between 10,000BC and 2000 (3 + 3 marks)

Ageing Populations
Describe the consequences (benefits and problems) of ageing populations
Ageing Populations
Describe the consequences (benefits and problems) of ageing populations
Figure 1. Population pyramid for Japan
Figure 2. Total population over time for Japan
Japan's population is changing.
Calculate the percentage of people aged 65+
Using the figure for total population, calculate the total number of people aged 65+
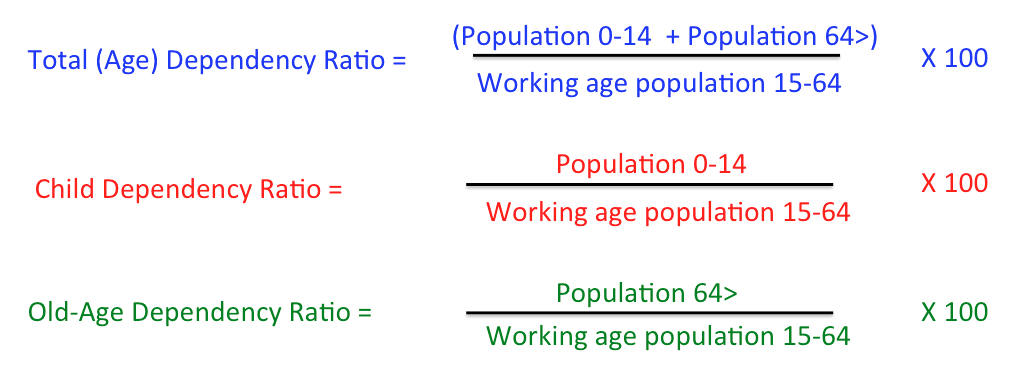
DEPENDENCY RATIO
The dependency ratio is an age-population ratio of those typically not in the labour force (the dependent part ages 0 to 14 and 65+) and those typically in the labor force (the productive part ages 15 to 64). It is used to measure the pressure on productive population and is shown as a percentage %.
How are total, child and old-age dependency ratios similar and different?
RUSSIA
Population: 142,257,519 (2017)
0-14 years: 24,352,817
15-64 years: 97,593,388
65 years and over: 20,311,314
SWITZERLAND
Population: 8,236,303 (2017)
0-14 years: 1,248,503
15-64 years: 5,493,092
65 years and over: 1,494,708
Calculate the total age dependency ratios for Switzerland and Russia.
Calculate the child dependency ratios for Switzerland and Russia.
Calculate the old-age dependency ratio for Switzerland and Russia.
EFFECTS OF A HIGH OLD-AGE DEPENDENCY RATIO
Explain four impacts of a high dependency ratio.
Lower Tax Revenues - retired people pay lower income tax. Therefore, the working age population has a greater responsibility to pay tax.
Higher Government Spending - the government is committed to paying a state pension and related benefits such as a minimum income guarantee. There are also greater demands for indirect spending on retired people. People over 65 are more likely to require treatment by the NHS. Therefore, there are greater demands placed on government spending by a rise in the dependency ratio.
Higher tax rates - because of reduced government finances, the working population pay more taxes. This could lead to people working less and reducing disposable income (savings). The government may be forced to collect more revenue from indirect taxes or wealth taxes.
Lower pension funds - because of the rising percentage of retired people, pension funds are having to stretch further than before. Many pension funds haven’t planned for the rapid rise in the dependency ratio. Combined with the credit crisis and low interest rates, the average income retired people can expect has fallen.
Pressure to raise retirement age - because of the increased cost of pensions there is pressure to raise the retirement age in both the private sector and public sector. Tesco’s recently announced it will be the first private firm in the UK to raise its pension age to 67. This is an attempt to reign in the costs and meet the pension shortfall they currently have.
Inequality - raising the state pension age will have different effects. Some people with a substantial private pension will not really be affected. They can still choose to retire when they want. However, others with no or minimal state pension will have to work longer.
CASE STUDY: JAPAN'S AGEING, DEPENDENT POPULATION
What challenges will Japan face as its population ages?
EXAM PRACTICE
With reference to named examples, examine the consequences (benefits and challenges) of an ageing population [7 marks]
The best answers will:
include frequent reference to facts, data and examples
compare both the benefits and challenges
come to a clear conclusion

Youthful Populations
Examine the impacts of a youthful population structure
Youthful Populations
Examine the impacts of a youthful population structure
Examine this population pyramid for Cambodia.
Explain how the following factors might have influenced the shape of this pyramid:
birth rates death rates infant mortality migration gender balance
2011 (Source)
Task
Use a pencil to draw a simple sketch map showing Cambodia’s location in South East Asia. Label neighbouring countries. Draw a box around your map.
Click to open
Read the infographic and create a factfile for Cambodia in your notes.
Add images to illustrate each of the points.
Highlight key information.
Write a paragraph introducing Cambodia and its youthful population.
the impacts (+&-) of Cambodia's youthful population
Watch the start of this documentary and note the positive and negative impacts of Cambodia’s youthful population.
TASK
Read pp 13-18 of the document
Describe the Cambodia’s demographic profile (pp 13-14)
Describe the challenges resulting from Cambodia's youthful population:
Economic & Social Context
Employment
Education
Health
Vulnerability
Participation & Rights
DEMOGRAPHIC DIVIDEND
Demographic dividend refers to the economic growth potential that can result from shifts in a population’s age structure, mainly when the share of the working-age population (15 to 64) is larger than the non-working-age share of the population (14 and younger, and 65 and older)".
In other words, it is “a boost in economic productivity that occurs when there are growing numbers of people in the workforce relative to the number of dependents.”
In order for economic growth to occur the younger population must have access to quality education, adequate nutrition and health including access to sexual and reproductive health.
TASK: Explain the causes of demographic dividend and what must be implemented to ensure that a country benefits from a youthful population
garment industry in cambodia

Copy of Country with High Dependant Population
Examine the impacts of a youthful population structure
Copy of Country with High Dependant Population
Examine the impacts of a youthful population structure
Examine this population pyramid for Cambodia.
Explain how the following factors might have influenced the shape of this pyramid:
birth rates death rates infant mortality migration gender balance
2011 (Source)
Task
Click to open
Read the infographic and create a factfile for Cambodia in your notes.
Add images to illustrate each of the points.
Highlight key information.
Write a paragraph introducing Cambodia and its youthful population.
the impacts (+&-) of Cambodia's youthful population
Watch the start of this documentary and note the positive and negative impacts of Cambodia’s youthful population.
TASK
Read pp 13-18 of the document
Describe the Cambodia’s demographic profile (pp 13-14)
Describe the challenges resulting from Cambodia's youthful population:
Economic & Social Context
Employment
Education
Health
Vulnerability
Participation & Rights
DEMOGRAPHIC DIVIDEND
Demographic dividend refers to the economic growth potential that can result from shifts in a population’s age structure, mainly when the share of the working-age population (15 to 64) is larger than the non-working-age share of the population (14 and younger, and 65 and older)".
In other words, it is “a boost in economic productivity that occurs when there are growing numbers of people in the workforce relative to the number of dependents.”
In order for economic growth to occur the younger population must have access to quality education, adequate nutrition and health including access to sexual and reproductive health.